Understanding Wound Debridement
Wound debridement is a medical process designed to remove dead, damaged, or infected tissue from a wound so that healing can occur more effectively. When a wound is left untreated or healing is delayed, necrotic tissue can form, creating a barrier that prevents new cells from regenerating. This buildup also increases the risk of infection, making it necessary to carefully clear the wound bed. By removing unhealthy tissue, healthcare providers create an environment that supports faster recovery and reduces the likelihood of severe complications. Wound debridement has been a vital component of wound care for decades, and it continues to evolve with modern medical practices. For patients living with chronic wounds or those with injuries that simply do not heal as expected, this procedure can be life-changing. Ultimately, the goal is to restore proper tissue function, promote comfort, and improve overall well-being.
Types of Wounds That May Require Debridement
Not all wounds require debridement, but certain conditions make it essential. Chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, venous ulcers, and pressure sores are among the most common cases where this procedure is necessary. These wounds often fail to heal on their own and can quickly become infected without intervention. Traumatic injuries, surgical wounds that develop complications, and severe burns may also require debridement to clear damaged tissue. Patients with compromised immune systems or poor circulation often face slower healing, making debridement a critical part of their recovery. A healthcare professional is best suited to evaluate whether a wound requires debridement, since untreated necrotic tissue can pose serious health risks. Recognizing these types of wounds early ensures timely treatment and better healing outcomes.
Methods of Wound Debridement
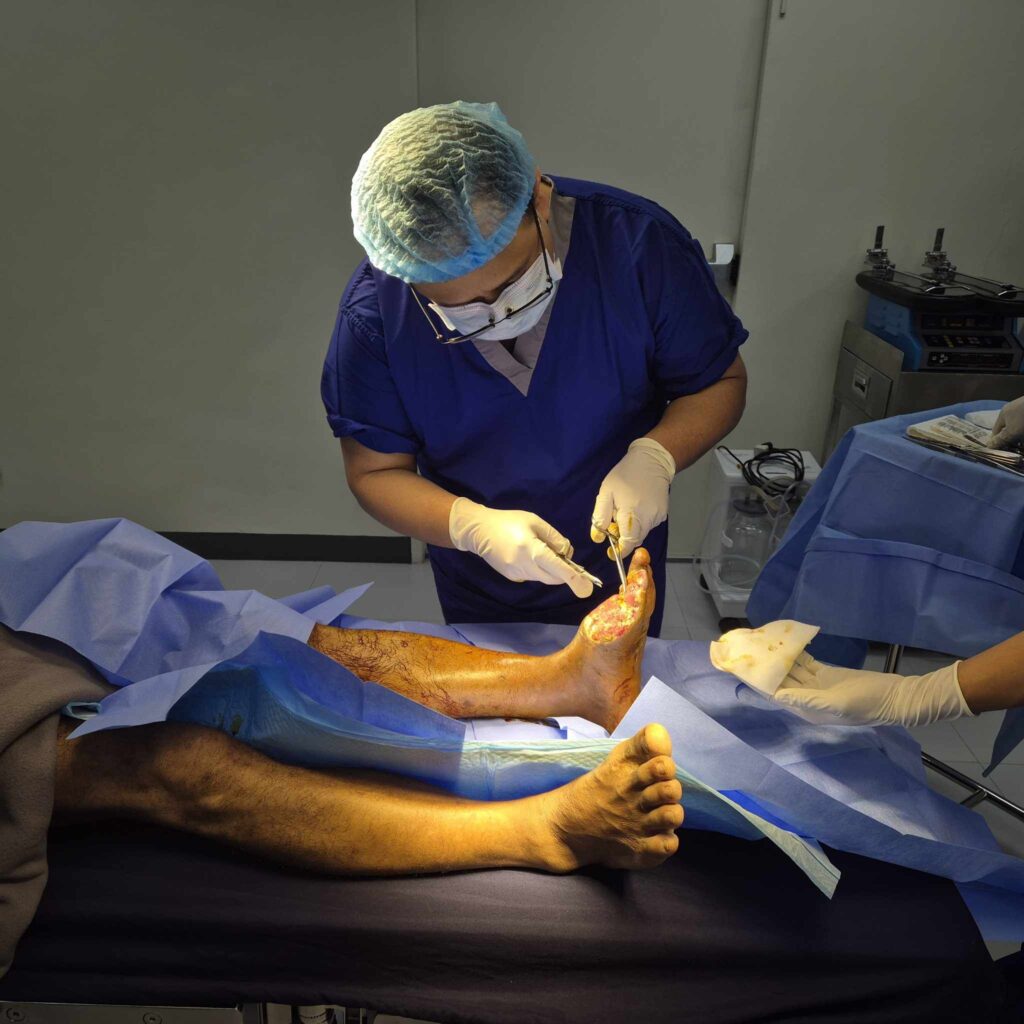
There are multiple techniques for wound debridement, each with specific benefits and applications depending on the patient’s condition. Surgical or sharp debridement is one of the fastest methods, performed by a doctor or surgeon who carefully removes necrotic tissue with precision instruments. Autolytic debridement allows the body to naturally break down dead tissue using moisture-retentive dressings that encourage healing. Enzymatic debridement involves applying topical agents to the wound, which chemically dissolve necrotic tissue without harming healthy cells. Mechanical debridement, often involving irrigation, hydrotherapy, or wet-to-dry dressings, uses physical force to remove dead tissue but can sometimes be more uncomfortable. Biological debridement, also known as maggot therapy, introduces sterile larvae that safely consume necrotic tissue while leaving healthy tissue intact. Each method has its own advantages and is selected based on the wound type, patient comfort, and healing goals.
Factors Determining the Best Debridement Method
Choosing the right approach depends on several key factors that must be considered by healthcare providers. The type of wound, its depth, and the amount of necrotic tissue present will often dictate the most effective method. Patients with underlying conditions such as diabetes, vascular disease, or compromised immunity may require more careful techniques to avoid complications. Tolerance levels also matter, as some methods may cause more discomfort than others. Cost and accessibility play a role too, since not all treatments are available in every setting. Finally, the overall healing potential of the patient guides decision-making, ensuring the chosen method aligns with both short-term recovery and long-term health. These factors make professional evaluation critical in determining the safest and most effective course of action.
Risks and Considerations in Wound Debridement
Although wound debridement offers significant benefits, it also carries certain risks that patients should understand. Discomfort or pain during the procedure is possible, especially with mechanical or surgical methods. There is also a small risk of bleeding, particularly if the wound is deep or located near major blood vessels. Infection is another consideration, though proper sterilization and professional care significantly reduce this risk. For patients with weakened immune systems, debridement requires extra caution to prevent complications. Some individuals may experience slower healing if underlying health conditions are not managed properly. It is important to follow post-procedure care instructions closely, as this minimizes risks and ensures optimal healing. Overall, the benefits of debridement often outweigh the risks when conducted by trained professionals.
Role of Wound Debridement in Healing Outcomes
Proper debridement plays a critical role in accelerating healing and restoring tissue health. By clearing away necrotic tissue, the wound bed becomes more receptive to new cell growth and blood supply. This improves oxygen delivery and nutrient absorption, both of which are vital for tissue regeneration. Patients with chronic wounds often experience noticeable improvements in healing rates once debridement is performed. In high-risk individuals, such as those with diabetes, this procedure can reduce the likelihood of severe complications like amputation. Beyond the physical benefits, effective wound healing also improves quality of life by reducing discomfort and restoring mobility. When wounds heal properly, patients can return to daily activities with confidence and reduced anxiety. The overall impact of debridement on recovery outcomes makes it an indispensable part of modern wound care.
Post-Debridement Care and Management
After wound debridement, proper care is essential for ensuring recovery continues smoothly. Dressings must be applied correctly to maintain a moist environment that promotes healing while protecting against infection. Wound cleansing and dressing changes are typically performed regularly to monitor progress. Patients are often advised on how to prevent infection through good hygiene practices and wound monitoring. Nutritional support is also important, as adequate protein, vitamins, and hydration directly affect tissue repair. Healthcare providers may recommend specific medications or topical treatments to further aid healing. Regular follow-up appointments allow specialists to track the wound’s progress and adjust treatment as needed. Adhering to these guidelines ensures the wound heals efficiently and reduces the chance of complications.
Advanced Techniques and Innovations in Wound Debridement
Medical advancements have introduced new approaches that enhance the effectiveness of debridement. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses suction to remove fluids and encourage blood flow, supporting faster healing after debridement. Some therapies combine debridement with growth factors or bioengineered skin substitutes, creating a more favorable healing environment. Enzymatic and biological debridement methods continue to evolve, offering patients less invasive options with effective results. Emerging technologies also include laser-assisted debridement and ultrasonic devices that provide greater precision. These innovations are particularly useful for patients with complex wounds that do not respond well to traditional treatments. By integrating advanced techniques, healthcare providers can offer more personalized and effective wound care. Future developments are likely to expand these options even further, making debridement safer and more efficient.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to seek medical evaluation for a wound is crucial to prevent complications. If a wound does not show signs of healing within two weeks, professional care may be necessary. Redness, swelling, foul odor, or discharge are warning signs of infection that should not be ignored. Pain that worsens over time or blackened tissue around the wound are also red flags that indicate necrosis. Patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes should be especially vigilant, as minor wounds can escalate quickly. A wound care specialist or physician can assess the situation and determine if debridement is required. Seeking timely treatment improves healing outcomes and reduces risks of severe complications. Relying on expert guidance ensures that the wound is managed safely and effectively.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Wound Debridement
Despite its importance, wound debridement is often misunderstood by patients and caregivers. One common misconception is that the process is always extremely painful, when in fact, many methods are designed to minimize discomfort. Another myth is that home remedies or over-the-counter creams can replace professional debridement, which is not true for serious or chronic wounds. Some believe that once a wound is cleaned, it does not require further monitoring, but ongoing care is essential for proper healing. There are also misunderstandings about the role of dressings, with many assuming they are just to cover the wound rather than actively aid healing. Education about these misconceptions helps patients feel more comfortable and confident when undergoing treatment. Addressing these myths ensures patients receive accurate information and better care outcomes.
FAQ Section
What is the fastest method of wound debridement?
Surgical or sharp debridement is considered the fastest method, as it removes necrotic tissue immediately and prepares the wound bed for healing.
Is wound debridement painful?
Some methods may cause discomfort, but healthcare providers often use anesthesia or pain management techniques to minimize discomfort.
Can wound debridement be done at home?
Debridement should only be performed by trained professionals. Attempting to do it at home can increase the risk of infection and worsen the wound.
How long does it take for a wound to heal after debridement?
Healing time depends on the wound’s size, type, and the patient’s overall health. Some wounds may take weeks to months to fully heal.
Who performs wound debridement procedures?
Debridement is usually performed by wound care specialists, nurses, or surgeons trained in wound management.
Takeaway
Wound debridement is a crucial medical process that removes necrotic tissue and creates the foundation for proper healing. With multiple methods available, from surgical to biological approaches, healthcare providers select the most suitable option based on patient needs and wound conditions. While there are risks, professional evaluation ensures the safest and most effective outcomes. Post-debridement care, innovations in wound management, and early recognition of complications all contribute to successful recovery. By understanding its importance, patients and caregivers can take proactive steps toward achieving better healing and improving quality of life.