Understanding Non-Healing Wounds
When most people think of a wound, they imagine a scrape, cut, or injury that heals within days or weeks. However, some wounds persist far longer than expected and are classified as non-healing. A non-healing wound typically does not show significant improvement after four to six weeks of proper care, which makes it a serious medical concern. The causes of non-healing wounds vary, but some of the most common include poor circulation, diabetes, infections, immune system issues, and complications involving bones, joints, or muscles. Orthopedic factors, such as fractures or bone exposure, can make it even more difficult for the body to repair itself naturally. Signs that a wound may require specialized orthopedic treatment include persistent swelling, pain, drainage, or visible bone and tendon exposure. Seeking early treatment is essential, as untreated wounds can lead to dangerous complications that affect overall health and mobility.
The Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Treating Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic specialists bring a unique perspective to the management of non-healing wounds because they focus on the body’s musculoskeletal system. While a general physician may treat the surface of a wound, an orthopedic doctor investigates whether structural or mechanical issues are interfering with healing. For example, a wound on the foot may be slow to heal due to poor alignment, pressure from walking, or complications from a fracture. Orthopedic doctors are skilled in identifying these contributing factors and creating treatment plans that address both the wound and its root cause. Collaboration is also a key part of their work, as they often coordinate with vascular surgeons, endocrinologists, and wound care nurses to provide comprehensive patient care. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of a patient’s condition are evaluated. In many cases, the involvement of an orthopedic specialist is what makes the difference in turning a chronic wound into one that finally begins to heal.
Advanced Orthopedic Treatment Options for Non-Healing Wounds
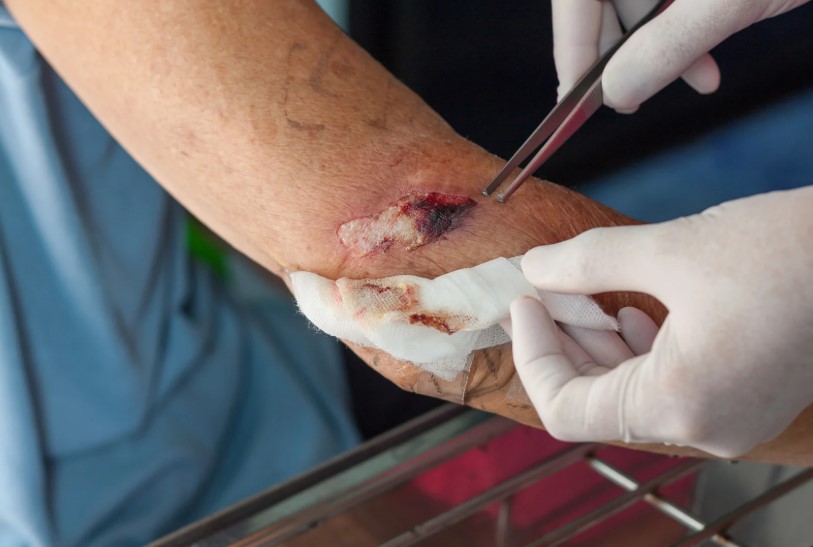
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds often involves advanced surgical and medical techniques designed to stimulate healing. Surgical debridement, where dead or infected tissue is carefully removed, helps create a clean environment for new tissue to grow. In cases where wounds are large or expose bone, skin grafts or flap surgery may be necessary to close the wound and protect underlying structures. Orthopedic reconstruction may also be required for wounds associated with fractures, severe trauma, or bone infections. In some cases, implants, external fixators, or braces are used to stabilize the affected area, giving the wound a chance to recover without constant stress or movement. Regenerative medicine, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy, is another area showing promising results, as it helps accelerate natural healing processes. Additionally, some orthopedic patients may benefit from hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which increases oxygen supply to the wound, promoting tissue repair. Each of these treatments is carefully chosen based on the severity of the wound and the patient’s overall health condition.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Interventions
Not all orthopedic treatments for non-healing wounds require surgery, and many patients find relief through non-invasive or minimally invasive options. One of the most important interventions is offloading, which means reducing the pressure placed on a wound through the use of casts, braces, or specialized orthopedic footwear. By minimizing stress on the wound, healing can progress more effectively. Physical therapy is also a valuable tool, as it improves circulation, strengthens surrounding muscles, and enhances mobility while protecting the wound site. Orthopedic wound dressings, made from advanced materials, are specifically designed to create a healing environment by maintaining moisture balance and preventing infection. Pain management strategies, including medications and nerve treatments, are often incorporated to ensure patients can tolerate care and maintain their quality of life. In some situations, customized orthotics and footwear adjustments can prevent recurring pressure sores or diabetic foot ulcers. These non-surgical strategies not only encourage wound recovery but also empower patients to remain active and independent while receiving treatment.
Risks of Leaving Non-Healing Wounds Untreated
Delaying treatment for non-healing wounds can have serious and long-lasting consequences. One of the most severe risks is the development of chronic infections such as osteomyelitis, which occurs when bacteria spread to the bone. Once infection reaches this stage, it becomes much harder to treat and may require extensive orthopedic surgery. Non-healing wounds, particularly in diabetic patients, can also increase the risk of amputation, dramatically affecting mobility and independence. Beyond physical risks, these wounds can significantly impact a person’s emotional and mental well-being, as chronic pain and immobility often lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. Untreated wounds may also interfere with work, daily activities, and relationships, lowering overall quality of life. From a financial perspective, the longer a wound remains untreated, the higher the medical costs for surgeries, hospital stays, and medications. Taking prompt action with orthopedic treatment is one of the most effective ways to avoid these devastating outcomes and protect long-term health.
Lifestyle and Preventive Strategies Supported by Orthopedics
Preventing non-healing wounds or supporting recovery often requires adjustments to lifestyle habits, many of which can be guided by an orthopedic specialist. Nutrition plays a critical role, as the body needs adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals to repair tissues. Patients are often encouraged to adopt a balanced diet that includes nutrients such as vitamin C, zinc, and iron. Movement and exercise under orthopedic supervision can also improve blood circulation, prevent stiffness, and reduce the likelihood of pressure-related wounds. For individuals with diabetes or circulation problems, proper footwear is one of the simplest yet most effective preventive strategies, as it minimizes pressure points and reduces the risk of ulcers. Posture correction and physical therapy exercises also prevent wounds that result from repeated friction or poor alignment. Patient education is another essential element, as learning how to monitor wounds daily and recognize warning signs can prevent small problems from becoming serious medical conditions. By combining orthopedic guidance with healthy daily practices, patients are more likely to achieve lasting healing and reduce the chance of wound recurrence.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Specialist for Non-Healing Wounds
Finding the right orthopedic specialist can make all the difference when dealing with a non-healing wound. Patients should look for doctors with experience in both orthopedic surgery and wound management, as this combination ensures comprehensive care. It is also important to choose a specialist who works within a hospital or clinic that has advanced wound care facilities, including hyperbaric oxygen chambers, surgical equipment, and rehabilitation services. During consultations, patients should feel comfortable asking questions about available treatment options, expected recovery times, and potential risks. A good orthopedic specialist will take the time to explain each step of the treatment plan and involve patients in decision-making. Ongoing care and regular follow-up visits are crucial, as wounds require continuous monitoring to ensure progress. Many patients benefit from a long-term relationship with their orthopedic doctor, which provides consistency and confidence in their care. Ultimately, choosing the right specialist not only improves outcomes but also offers peace of mind throughout the healing journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What makes orthopedic treatment different from general wound care?
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds goes beyond the surface of the skin, addressing deeper structural issues like bones, joints, and soft tissues. This ensures that the wound heals from the inside out, preventing recurring problems.
2. Can orthopedic treatment help diabetic patients with non-healing wounds?
Yes, orthopedic care is particularly important for diabetic patients, especially those with foot ulcers. Orthopedic specialists can reduce pressure on wounds, improve alignment, and provide advanced treatments that lower the risk of amputation.
3. How do orthopedic specialists determine whether surgery is necessary?
The decision depends on the wound’s severity, depth, and risk of infection. Orthopedic doctors may recommend surgery if conservative treatments fail or if there is bone exposure, tissue death, or a high risk of complications.
4. What are the latest advancements in orthopedic wound healing treatments?
Some of the most promising advancements include regenerative therapies like platelet-rich plasma (PRP), stem cell therapy, and the integration of hyperbaric oxygen therapy with orthopedic care. These options stimulate faster tissue repair and reduce complications.
5. How long does it typically take for an orthopedic-treated wound to heal?
Healing times vary depending on the patient’s overall health, the severity of the wound, and the treatment approach. While some wounds improve within weeks, others may require months of specialized care and monitoring.
6. Are there non-invasive orthopedic treatments available for non-healing wounds?
Yes, many patients benefit from non-surgical methods such as braces, orthotics, physical therapy, and advanced wound dressings. These treatments help create an environment for healing while reducing stress on the wound site.