Diabetes-related foot infections are a serious concern for individuals managing diabetes. Without prompt treatment, these infections can lead to complications that impact both quality of life and mobility. Orthopedic treatment plays a crucial role in managing diabetes-related foot infections, helping to preserve tissue health, reduce infection spread, and improve mobility. In this blog, we’ll explore how orthopedic care supports the healing process and helps prevent severe complications for those suffering from diabetes-related foot issues.
What Is Diabetes-Related Foot Infection?
A diabetes foot infection is a condition that occurs when a wound or ulcer on the foot becomes infected due to the compromised blood circulation and nerve damage commonly associated with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves (neuropathy) and restrict blood flow, making it more difficult for wounds to heal. This creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to infections.
Symptoms of diabetes-related foot infections may include redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes discharge from the wound. Left untreated, these infections can progress to more severe conditions, including tissue death or even amputation in extreme cases.
Importance of Orthopedic Care in Treating Diabetes-Related Foot Infection
Orthopedic care is essential in treating diabetic foot infections to prevent the infection from spreading, promote faster healing, and improve overall mobility. Orthopedic specialists focus on maintaining the integrity of the foot while ensuring that any damaged tissue is carefully treated or removed to prevent further harm.
Orthopedic care for foot infections typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Wound care and management
- Debridement (removal of dead or infected tissue)
- Prevention of deformities that may arise due to nerve damage or infection
The goal is to restore foot health, minimize complications, and ultimately preserve mobility for patients suffering from diabetic foot problems.
Common Causes of Diabetes-Related Foot Infections
Several factors contribute to the development of diabetic foot infections, including:
- Poor circulation: Diabetes can cause the blood vessels in the feet to narrow, reducing blood flow. This limits the body’s ability to fight infections and heal wounds.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage often results in reduced sensation, meaning individuals may not feel pain or discomfort from minor injuries that could develop into infections.
- Pressure ulcers and wounds: Due to poor circulation and neuropathy, wounds can form on the feet, often without the person realizing it, allowing bacteria to enter.
The risk factors associated with diabetic foot infections highlight the importance of regular monitoring and proactive care. People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for signs of injury or infection to catch issues early.
Orthopedic Treatment Options for Diabetes-Related Foot Infection
There are several orthopedic treatment options available to manage diabetic foot infections effectively. These treatments focus on healing the infection, promoting tissue preservation, and improving the overall function of the foot.
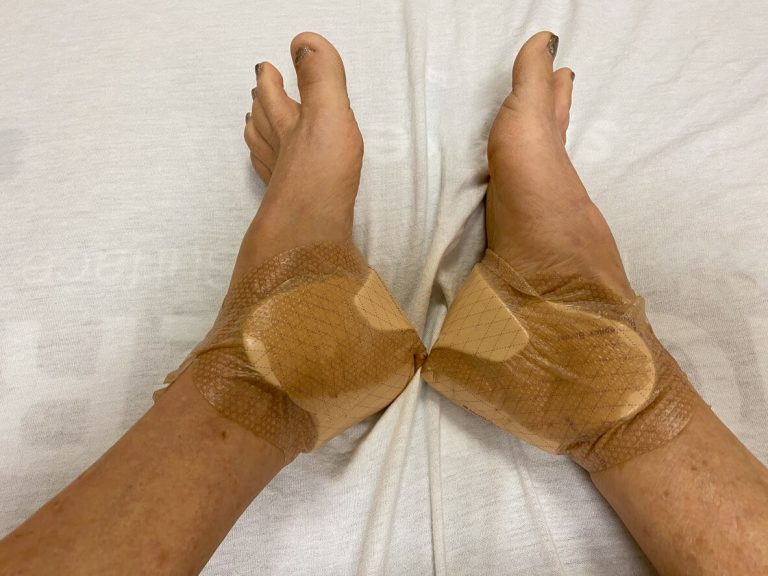
- Wound care: Orthopedic specialists provide thorough wound management, including cleaning, dressing, and protecting the wound to prevent further infection.
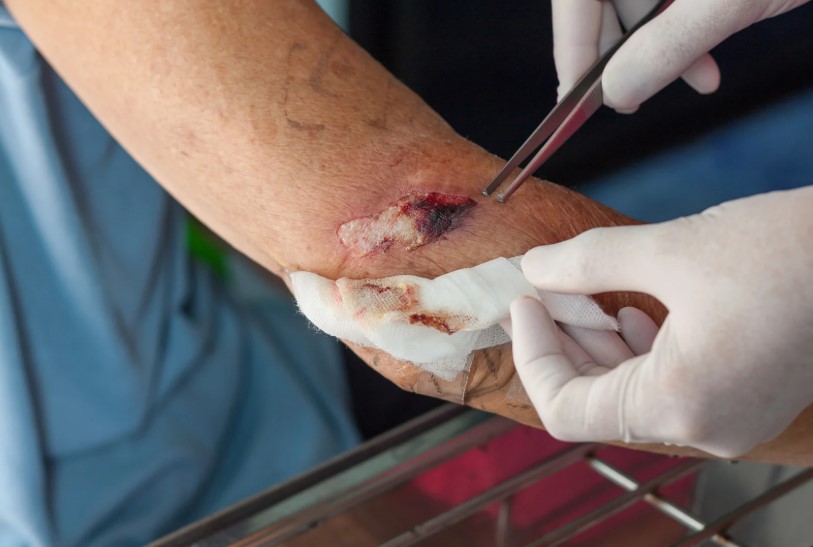
- Debridement: When necessary, orthopedic surgeons will remove dead tissue to allow healthy tissue to regenerate and heal the infection.
- Antibiotic therapy: Oral or intravenous antibiotics may be prescribed to fight the bacterial infection and prevent it from spreading.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove infected tissue or address complications like abscesses or gangrene.
- Orthotic devices: Custom-made shoes or insoles may be used to relieve pressure on the feet, reducing the risk of additional wounds or ulcers.
These specialized treatments help improve the chances of a full recovery and prevent the need for more invasive procedures, such as amputations.
How Orthopedic Care Promotes Healing and Prevents Complications
Orthopedic care for diabetic foot infections not only helps manage infection but also works to preserve healthy tissue and promote healing. The debridement process ensures that the body is left with healthy, viable tissue capable of healing, while the use of orthopedic devices can reduce stress and pressure on the feet, giving them the best chance to recover.
By targeting the root causes of infections—such as poor circulation and neuropathy—orthopedic specialists can prevent infections from worsening and help avoid complications like gangrene or the need for amputation. The preservation of healthy tissue through careful treatment is key to a positive outcome and recovery.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Regular Monitoring
One of the most critical aspects of treating diabetes-related foot infections is early intervention. Addressing infections early can prevent them from escalating into more severe complications. Diabetic patients should check their feet daily for cuts, blisters, or signs of infection and seek medical help promptly if any issues arise.
Regular visits to an orthopedic specialist for foot health monitoring are also essential for managing the risk of infection and ensuring that foot problems are addressed before they become more serious. The earlier an infection is treated, the less likely it is to cause permanent damage.
Preventing Future Foot Infections in Diabetic Patients
Prevention is always better than cure. For individuals with diabetes, taking steps to prevent future foot infections can make a significant difference in maintaining good foot health. Here are some foot care tips for diabetes:
- Proper hygiene: Keep feet clean and dry to avoid infections. Use a mild soap and dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Moisturize: Use lotions to prevent cracked skin, but avoid moisturizing between the toes where fungal infections can develop.
- Check feet daily: Inspect feet regularly for cuts, sores, blisters, and any signs of infection.
- Wear proper footwear: Opt for comfortable, well-fitting shoes and use insoles or custom orthotics to reduce pressure points.
- Manage blood sugar levels: Maintaining good blood sugar control can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of nerve damage.
Education and proactive management can significantly reduce the chances of developing diabetic foot infections and improve overall health outcomes.
Takeaway
Orthopedic treatment for diabetes-related foot infection is crucial for managing the infection, promoting healing, and preventing complications. Early intervention, wound care, and specialized treatments like debridement and orthotic devices are all vital tools in helping individuals with diabetes maintain good foot health. Regular monitoring and preventive care are key to reducing the risk of infection and preserving mobility.