In orthopedics, treating infections that arise from traumatic injuries or surgical procedures is crucial to a successful recovery. The right orthopedic treatment for infected wounds can help prevent serious complications and ensure the healing process is as smooth as possible. Traumatic and surgical wounds are particularly prone to infection due to exposure to bacteria, and without proper intervention, these infections can spread, leading to long-term issues. In this article, we explore the orthopedic solutions available for treating these infections and how timely care can help safeguard your health.
Understanding Traumatic and Surgical Wound Infections
What are Traumatic and Surgical Wound Infections?
Traumatic and surgical wounds, although common, are vulnerable to infection if not treated properly. A traumatic wound can be caused by an accident or injury, while a surgical wound is the result of an operation. In both cases, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is critical to prevent complications such as bone infections or systemic infections. Infections may arise when bacteria enter the wound through an open cut, during surgery, or even from poor post-operative care.
Common Symptoms and Risks
Signs of an infected wound include swelling, redness, increased pain, and sometimes fever. If left untreated, these infections can lead to severe conditions like osteomyelitis (bone infection), which can make the recovery process much more challenging. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is designed to address these symptoms and halt the progression of infection, ensuring that the patient does not suffer long-term consequences.
Importance of Timely Intervention in Orthopedic Wound Infections
The Critical Role of Early Detection
Detecting infections early is vital in providing the right orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Early detection helps prevent the infection from spreading deeper into the tissues or bones. Once an infection begins to spread, treatment becomes more complex and may involve additional surgeries or prolonged antibiotic therapy. By ensuring a prompt response, the risk of complications such as permanent tissue damage or even amputation can be significantly reduced.
Prevention Methods
Preventing infections is equally important in the management of wounds. Proper wound care, including keeping the wound clean and dry, is essential. Additionally, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds often involves the use of antibiotics to combat bacteria before they cause a full-fledged infection. Hygiene practices, both before and after surgery, play a vital role in reducing the risk of infection and ensuring a quicker recovery.
Orthopedic Solutions for Treating Traumatic and Surgical Wound Infections
Antibiotic Therapy
When an infection is detected, one of the first lines of defense is antibiotic therapy. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds often includes the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics to fight off a range of bacteria. Depending on the results of bacterial cultures, more targeted antibiotics may be prescribed. Timely administration of antibiotics can prevent the infection from worsening and help the body fight off the bacteria more effectively.
Wound Care Techniques
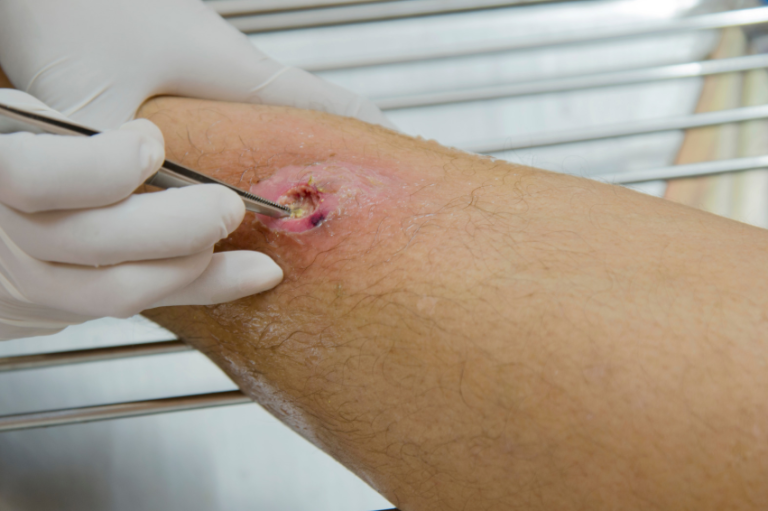
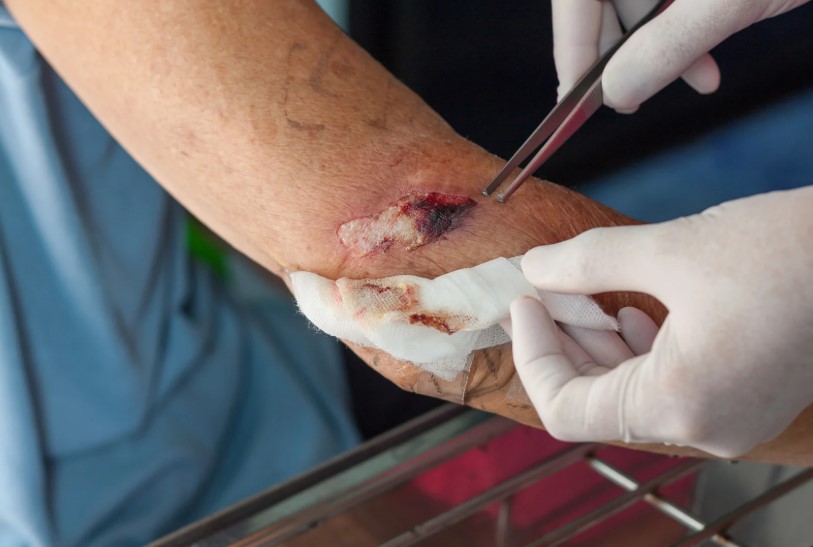
Proper wound care is essential in any orthopedic treatment plan. Debridement, the process of removing dead tissue, is often required in the case of severe infections. In addition, using sterile dressings and regular cleaning helps to prevent further contamination. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds also involves monitoring the wound for signs of infection and providing care that promotes healing while preventing bacteria from gaining a foothold.
Surgical Intervention
In some cases, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds may require surgical intervention. This may include procedures such as incision and drainage, which help release infected fluid and relieve pressure from abscesses. For more severe cases, bone grafts or reconstructive surgery might be necessary to restore function and remove infected bone tissue. Surgical interventions ensure that the infection is fully addressed and that the wound heals as expected.
Orthopedic Devices for Infection Control
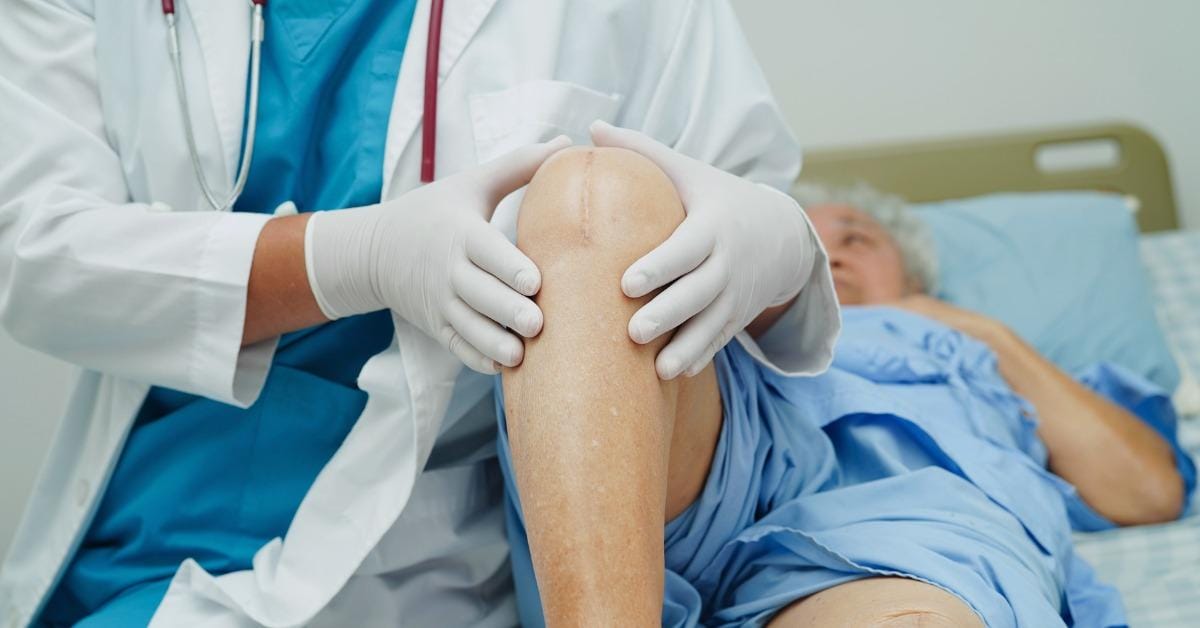
Certain orthopedic devices, such as external fixators and internal hardware, can be used to stabilize fractures while also preventing infection. These devices are designed to promote healing while minimizing the risk of infection. Some modern devices come with antimicrobial coatings that help reduce the likelihood of bacterial colonization. Using these advanced materials in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds can significantly enhance recovery outcomes and prevent complications.
Innovations in Orthopedic Infection Control
Emerging Technologies in Wound Healing
In recent years, there have been many advancements in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds, particularly in wound healing technologies. Bioactive dressings that release healing agents or antibiotics directly to the wound are helping speed up recovery. Additionally, phototherapy and electrical stimulation have been explored as ways to promote cell regeneration and reduce infection rates, improving outcomes for patients with difficult-to-treat wounds.
Personalized Approaches to Treatment
As technology advances, so does the ability to personalize treatment for infections. Genetic testing and bacterial culture analysis can now help tailor orthopedic treatment for infected wounds to better target the specific bacteria involved. This approach ensures that patients receive the most effective treatment plan, which is more likely to lead to a successful outcome.
Post-Treatment Care and Rehabilitation
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After infection treatment, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure that healing is progressing as expected. Regular follow-ups allow for early detection if the infection recurs, enabling prompt action and a more effective response. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds often includes post-operative care instructions and guidance on how to monitor for signs of reinfection.
Rehabilitation for Recovery
Following the treatment of an infected wound, rehabilitation is an important part of the recovery process. Physiotherapy plays a significant role in restoring function, mobility, and strength, particularly in cases where the infection has impacted the bones or joints. For many, a full recovery involves working closely with healthcare professionals to regain their pre-infection physical abilities, making orthopedic treatment for infected wounds a comprehensive approach that extends beyond infection control.
Takeaway
Addressing traumatic and surgical wound infections requires a multi-faceted approach, where early detection, proper care, and advanced treatments work together. Effective orthopedic treatment for infected wounds not only alleviates immediate infection symptoms but also supports long-term healing and recovery. If you experience signs of an infected wound, it’s essential to seek medical help promptly to ensure that you receive the appropriate treatment and minimize the risk of further complications. Consult an orthopedic specialist to find the best solutions tailored to your needs and start your journey to a full recovery.