Diabetic foot wounds are a common and serious complication that can dramatically affect the quality of life for individuals managing diabetes. These wounds often arise from minor injuries, pressure sores, or persistent ulcers, and when they become infected, the risk of severe complications increases. Expert care is essential to halt the progression of infection, preserve healthy tissue, and restore mobility. This article delves into the importance of specialized orthopedic care in managing these complex cases and highlights effective treatment strategies, preventive measures, and real-life success stories.
Understanding Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds
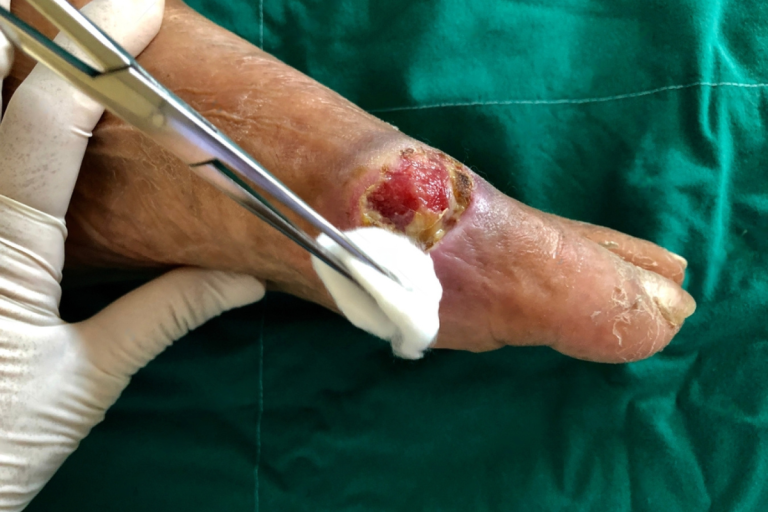
Diabetic foot wounds develop due to several factors linked to diabetes, including reduced blood circulation, nerve damage (neuropathy), and high blood sugar levels. These factors contribute to an environment where even small injuries can fail to heal properly. Infected diabetic foot wounds typically start as minor cuts, abrasions, or blisters that, when left untreated, can evolve into ulcers. The compromised blood flow prevents sufficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients needed for healing, while high glucose levels create an ideal setting for bacterial growth.
Poor circulation in diabetic patients not only slows the healing process but also limits the body’s ability to fight infections. As a result, a simple cut can lead to a deep-seated infection that jeopardizes the surrounding tissues. The ensuing infection may spread quickly, increasing the risk of complications such as cellulitis, osteomyelitis (bone infection), or even the need for amputation. Understanding these dynamics is crucial, as early intervention and specialized care are the cornerstones for effective management.
The Role of Orthopedic Intervention
Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds plays a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of these complications. Orthopedic specialists are uniquely equipped to address both the infection and its underlying structural issues. Their approach is comprehensive: it not only focuses on eliminating the infection but also on preserving as much healthy tissue as possible to maintain the patient’s mobility and overall function.
One of the primary goals of orthopedic intervention is to prevent the spread of infection. This is achieved through meticulous wound assessment, imaging studies, and, when necessary, surgical debridement to remove necrotic (dead) tissue. By controlling the source of the infection early, orthopedic surgeons help prevent the need for more drastic measures later on. Furthermore, these specialists integrate infection management with rehabilitative strategies, ensuring that patients can return to their daily activities with improved function and reduced pain.
Infection Management Strategies
Effective management of an infected diabetic foot wound begins with early diagnosis. Prompt recognition of infection signs—such as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain—is essential to prevent the progression of the condition. Once an infection is identified, the orthopedic team initiates a multi-pronged treatment approach:
- Debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue is often necessary to create an optimal healing environment. Surgical debridement is performed to minimize the bacterial load and expose healthy tissue.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Based on culture results, targeted antibiotics are administered to combat the specific pathogens responsible for the infection. In some cases, intravenous antibiotics may be required for severe infections.
- Advanced Wound Care: Utilizing modern dressings and wound care techniques, the orthopedic team can promote an environment that supports natural healing processes while protecting the wound from further contamination.
The integration of these strategies is critical for patients with diabetic foot wounds, where the risk of infection-related complications is particularly high. By combining early diagnosis with timely intervention, the treatment plan aims to halt infection spread and minimize tissue loss.
Tissue Preservation and Healing Techniques
A key focus of Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds is tissue preservation. Every effort is made to retain as much viable tissue as possible, which is crucial for maintaining function and ensuring long-term healing. Here are some of the techniques used:
- Precise Surgical Debridement: While it may be necessary to remove infected tissue, skilled orthopedic surgeons strive to conserve healthy tissue. This delicate balance minimizes the risk of destabilizing the foot’s structure.
- Wound Irrigation and Cleaning: Thorough cleaning of the wound helps remove debris and reduce bacterial load. Advanced irrigation techniques, sometimes using antimicrobial solutions, ensure that the wound environment is as clean as possible.
- Specialized Dressings: Modern wound care includes the use of advanced dressings that promote a moist wound environment, facilitate oxygen exchange, and protect against further bacterial invasion. These dressings often incorporate bioactive compounds that support cell growth and tissue regeneration.
- Adjunctive Therapies: In some cases, techniques such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) are employed to further stimulate tissue healing and reduce edema (swelling).
By focusing on tissue preservation, orthopedic specialists not only improve the healing process but also help maintain the structural integrity of the foot, thereby reducing the need for more radical interventions in the future.
Enhancing Mobility Through Orthopedic Treatment
Mobility is a significant concern for patients with diabetic foot wounds. Pain, loss of tissue, and structural changes in the foot can limit a person’s ability to walk and perform daily activities. Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds is designed not just to eliminate infection but also to restore and enhance mobility.
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: After initial treatment, patients often engage in a tailored rehabilitation program. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the muscles around the affected area, improving balance, and gradually increasing mobility.
- Custom Orthotics and Supportive Footwear: Orthopedic specialists may recommend custom orthotics or specially designed footwear to reduce pressure on the affected area, redistribute weight, and prevent further injury.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases where structural deformities contribute to mobility issues, corrective surgical procedures may be necessary. These interventions can realign bones, correct deformities, and improve overall foot function.
- Pain Management: Effective pain control is critical during the recovery process. Orthopedic care includes strategies for managing pain through medications, nerve blocks, or other advanced techniques.
Successful rehabilitation not only improves mobility but also enhances the overall quality of life, enabling patients to return to their daily routines with confidence.
Preventative Measures and Long-Term Care
Long-term management of diabetic foot health is vital for preventing future complications. Once the acute infection has been managed, orthopedic care emphasizes the importance of ongoing maintenance and preventive strategies:
- Daily Foot Care: Routine self-examinations and proper hygiene are essential. Patients are advised to inspect their feet daily for any signs of cuts, blisters, or abnormalities.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing diabetes through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper medication adherence plays a crucial role in preventing foot wounds. Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels helps reduce the risk of infection.
- Regular Check-Ups: Frequent visits to healthcare professionals, including orthopedic specialists, are recommended. These check-ups allow for early detection of potential issues before they evolve into serious complications.
- Patient Education: Empowering patients with knowledge about foot care, the importance of proper footwear, and warning signs of infection is a key component of long-term management.
These preventive measures are designed to minimize the likelihood of recurrence, ensuring that the benefits of initial treatment extend far into the future.
Takeaway
Managing infected diabetic foot wounds requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. Orthopedic Treatment for Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds is not only about treating an immediate infection; it’s about preserving tissue, restoring mobility, and preventing future complications. If you or a loved one is experiencing issues related to diabetic foot wounds, do not hesitate to seek specialized care. Early intervention, combined with a multi-disciplinary approach, can make a significant difference in outcomes.